EV charging levels can be classified as: Level 1, Level 2 and Level 3. Generally speaking, the higher the charging level, the higher the output power and the faster the EV charging speed. Of course, EV charging time is related to the type of car battery, battery capacity and the output power of the charging station, in addition to the charging level.
Level 1 charger: This type of charger plugs the EV directly into an electrical outlet through an AC power plug. The low power of a standard household outlet also means that charging an EV with this type of charger is very slow. In addition to the disadvantage of slow charging speed, safety is not guaranteed because there is no communication between the power outlet and the vehicle when using a Level 1 charger to charge an EV, which is a safety hazard. It is not recommended to use this charger for charging electric vehicles in non-essential situations, and this charger has been eliminated in many places.
Level 2 charger: This kind of charger is commonly used in residential, public parking lot, commercial place and other locations, usually installed in AC charging station, the output power is slightly larger than level 1 charger, the maximum output power can reach 22KW, the charging speed is much faster than level 1 charging. level 2 charging has certain safety features, which also makes some car owners invest in home AC charging station for electric car charging.
Level 3 charging station: Level 3 charging is the use of DC fast chargers for charging. Unlike Level 1 and Level 2 charging, Level 3 charging directly uses DC power to transfer electricity to the car battery, which has a faster charging speed.
Level 1, Level 2 and Level 3 charging talked about AC charging and DC charging above, and we all know that DC charging is faster. But in fact, no matter which charging level you choose to charge, the battery inside the electric car always needs to be charged with DC power. The difference between AC charging and DC charging is whether there is a conversion process or not. The difference between AC charging and DC charging is whether there is a conversion process. When using an AC charger to charge an electric car, the AC power is converted to DC power by the rectifier in the motor drive system. While when using a DC charger, the DC power does not go through the rectifier, it is directly into the battery.
EV charging plugs vary depending on the power output, the brand of the EV and the country and region where the car is manufactured.
Currently, several common AC charging plugs are as follows.
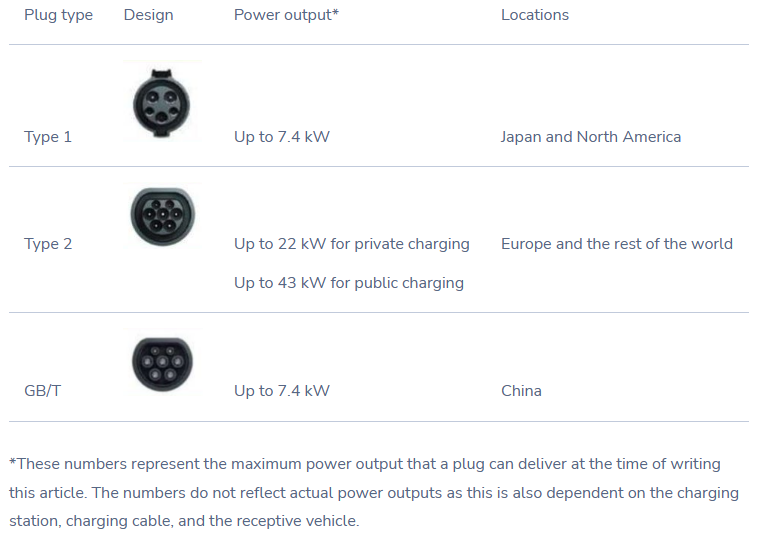
Currently, several common DC charging plugs are as follows.

FAFA-E offers Euro Mode 2 portable chargers; cable cords for Level 1 and Level 2 chargers, high power liquid-cooled charging cables for Level 3 chargers; in addition, we also produce EV connectors, including CCS1 connectors and CCS2 connectors, Charging station power outlet and other products.





 简体中文
简体中文
